
Diamonds are the hardest minerals in nature, essentially pure carbon crystals formed 150 to 300 kilometers below the Earths surface in the mantle. They crystallize over hundreds of millions of years under conditions of 1,100 to 1,600℃ temperature and 4.5 to 6GPa pressure. The GIA (Gemological Institute of America) notes that diamonds have a Moh’s hardness of 10, making them the only gemstone capable of scratching all natural substances.

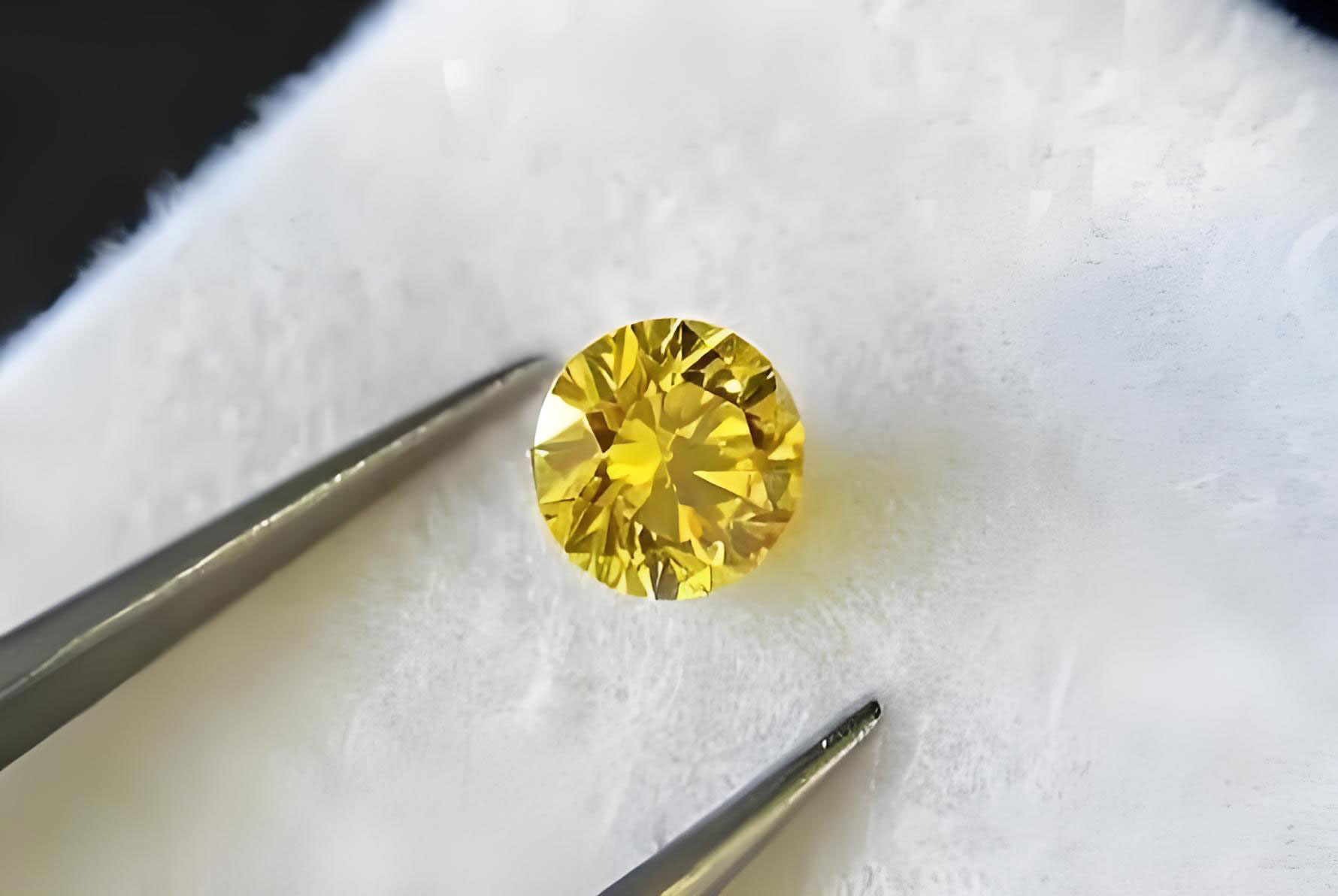
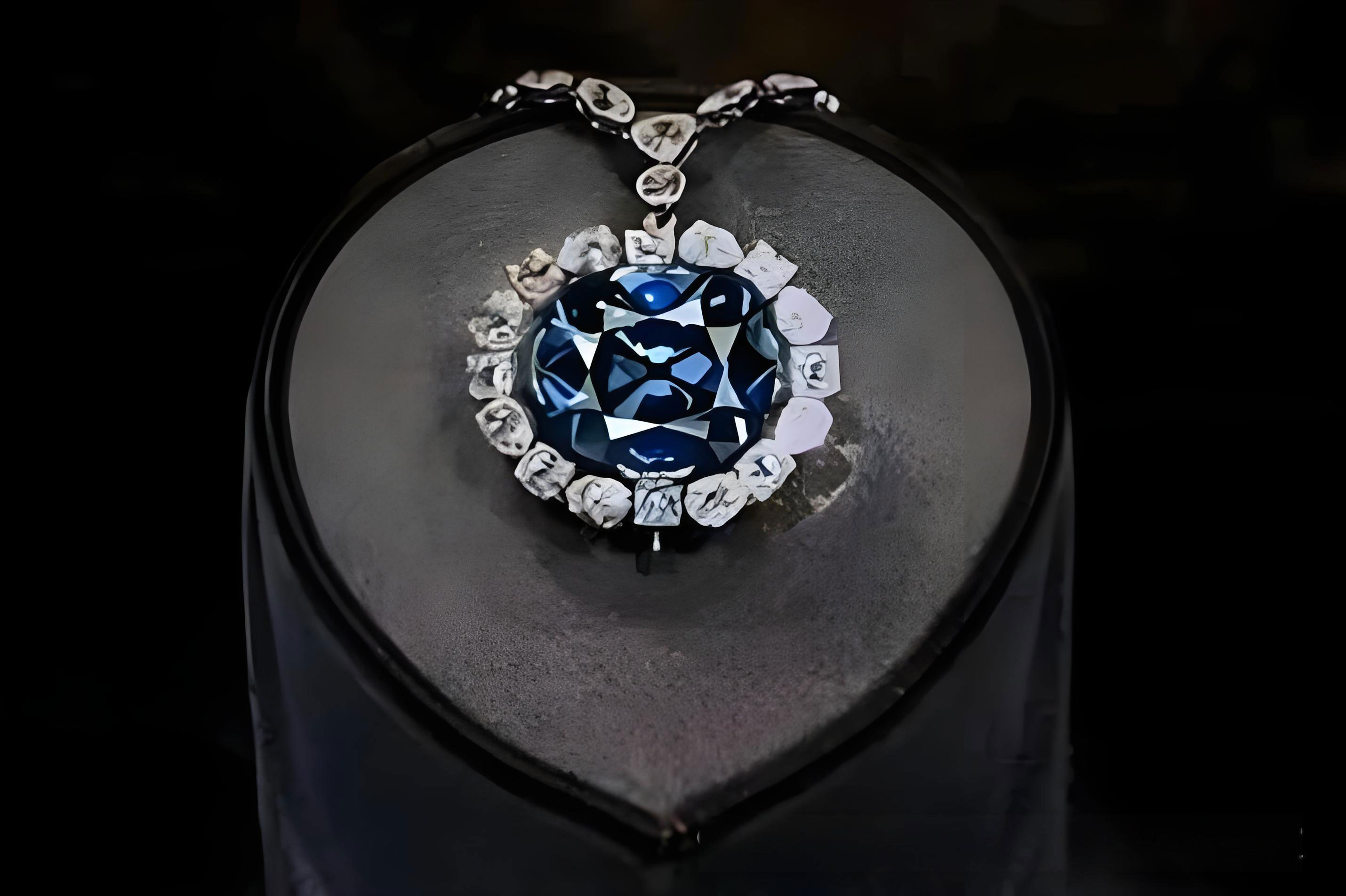
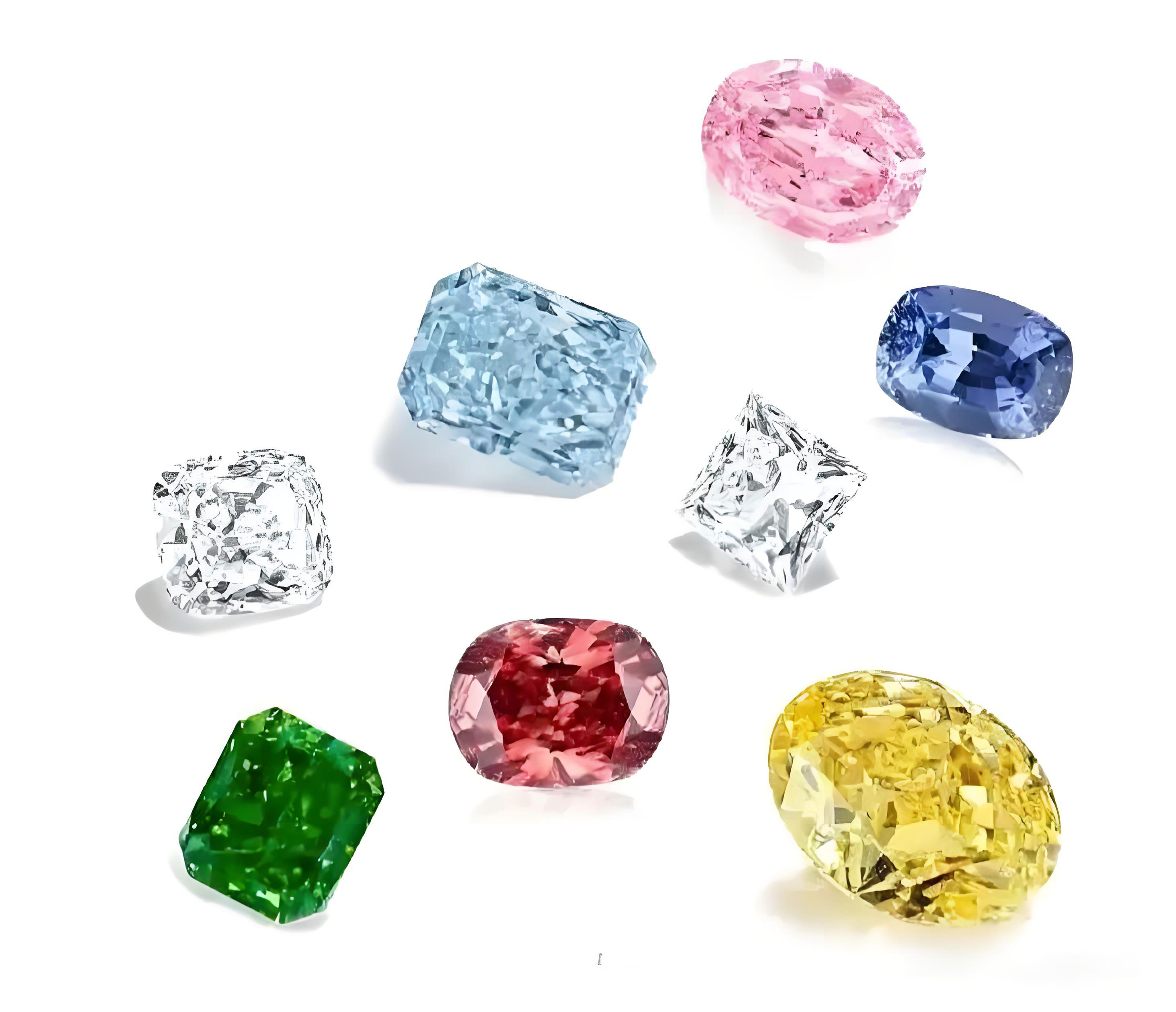
1. Physical Type a.Type I Diamond (with nitrogen): 98% of natural diamonds, including Type Ia (nitrogen polymer, such as ordinary white diamonds) and Type Ib (single atom nitrogen, rare canary yellow diamonds) b.Type II Diamonds (ultra-pure or boron-containing): Type IIa (impurity-free, such as the Cullinan diamond) and Type IIb (boron-induced blue, such as the legendary Hope diamond). 2. Color Classification a. Colorless series: D-Z color grading (GIA standard), D color is the top pure b.Color diamonds: Red diamond (lattice distortion), Yellow diamond (nitrogen element), Blue diamond (boron element), Green diamond (natural radiation), etc.




4th century BC: The worlds first diamond trade began in the Gorkanda mining area of India. 1477: Maximilian of Austria proposed marriage with a diamond ring, which created the tradition of diamond marriage. 1866: The modern diamond industry was born in the Kimberley mining area of South Africa. 1931: GIA was founded and developed the 4C grading system, which has become the gold standard for diamond identification worldwide.



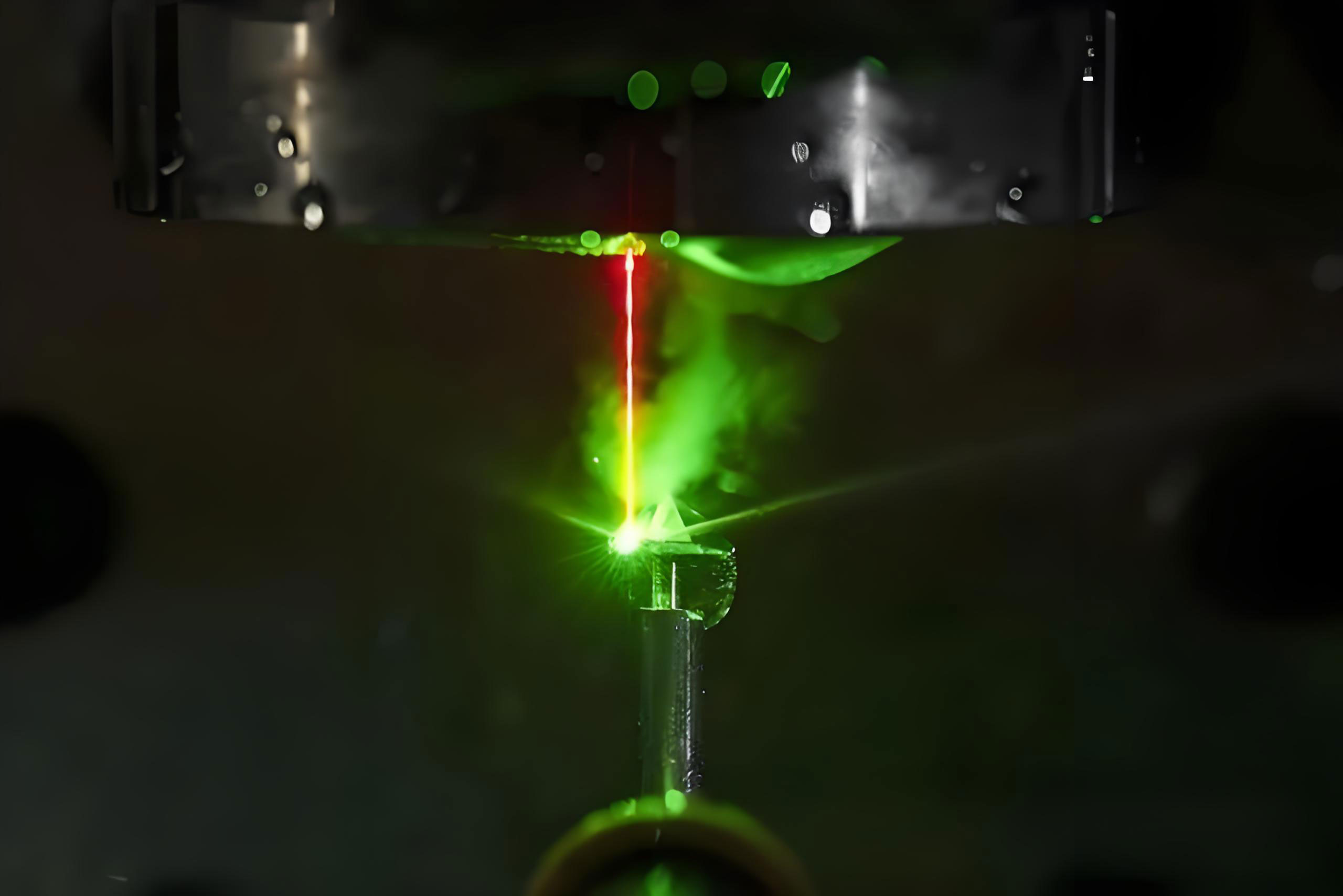
1. Cutting Process a.Traditional Five-step Method: Marking line, splitting, sawing, forming and polishing, 57-58 facets achieve standard round diamonds. b.Modern Breakthrough: Laser cutting technology achieves 0.02mm accuracy, 3D modeling to predict light efficiency.
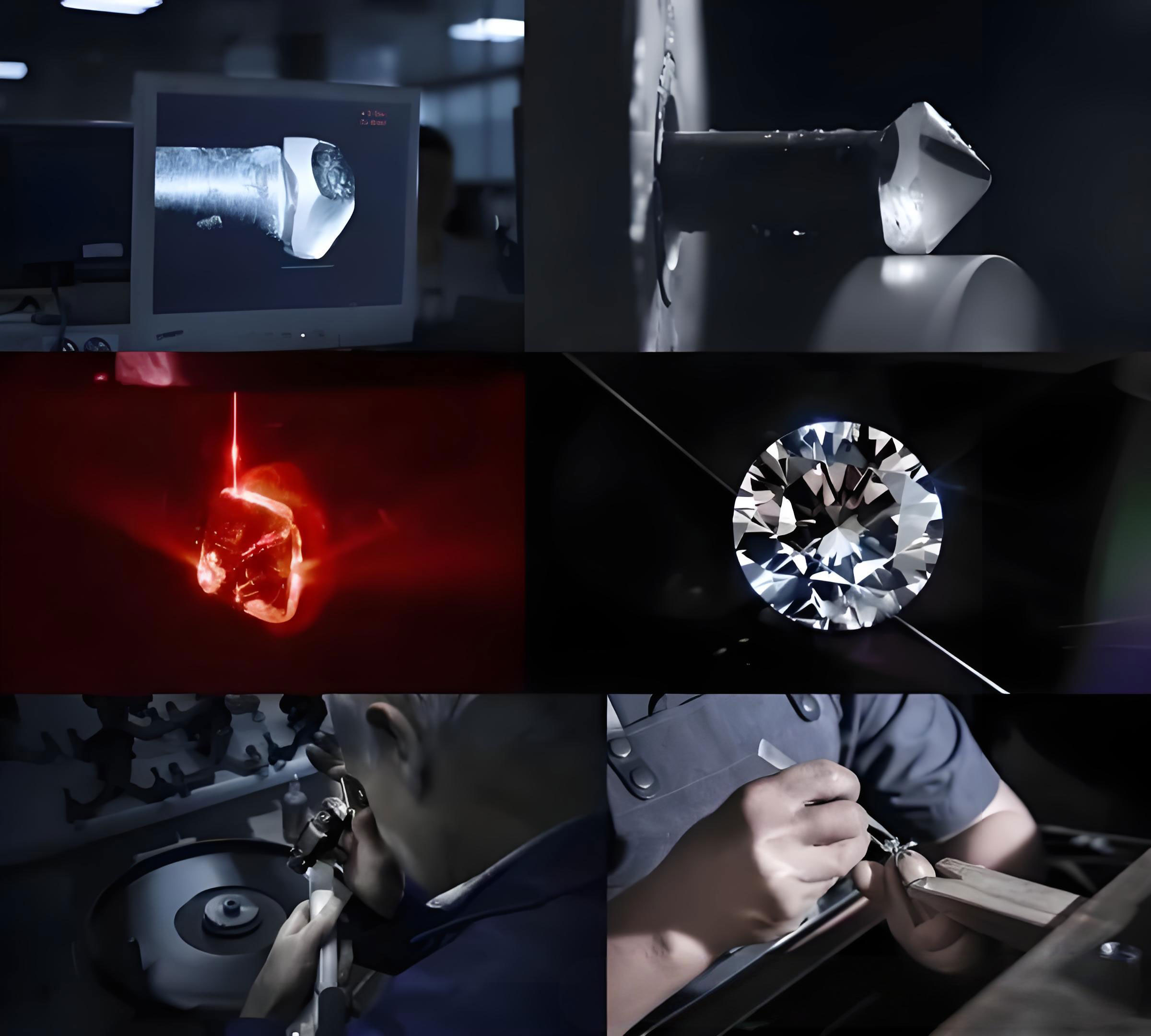

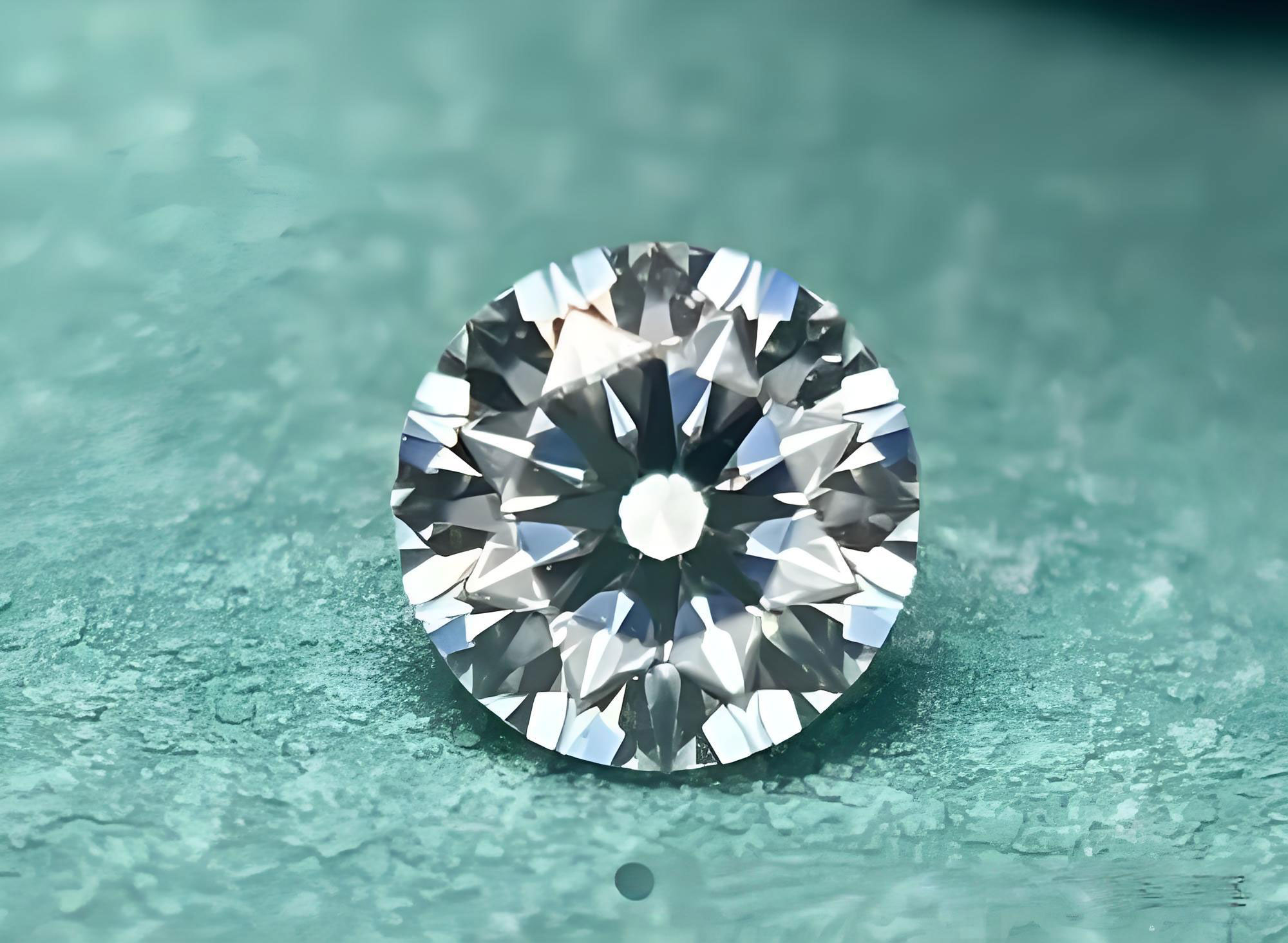
1.Color D-E-F is a collection grade colorless, and H color above has no yellow tone to the naked eye. 2.Clarity VVS grade (10x magnification without flaw) to SI grade (clean to the naked eye). 3.Cut 3EX (Excellent) cutting maximizes the light efficiency. 4.Carat 1 ct =0.2 g, the price increases exponentially with each additional 0.1 ct.
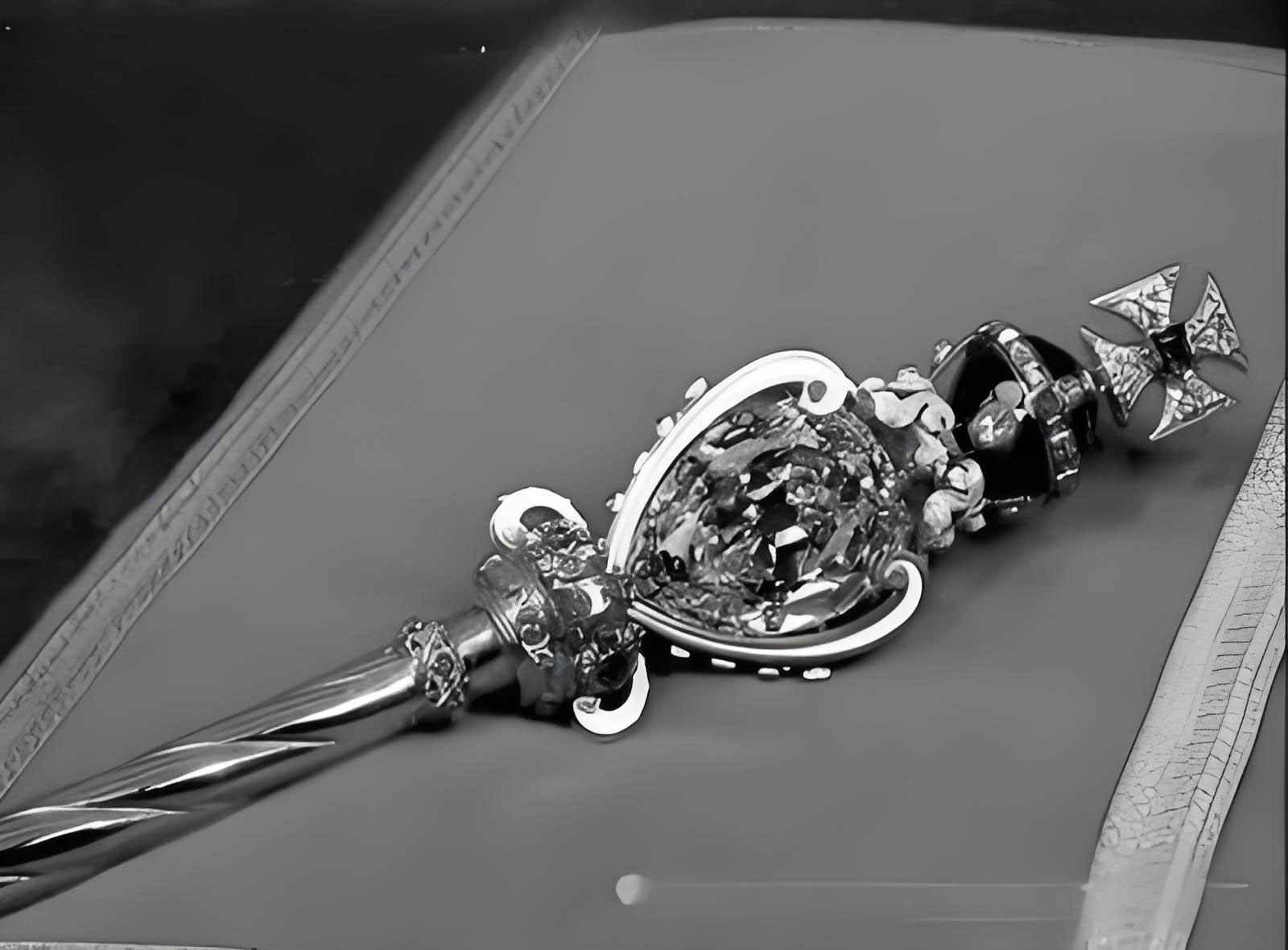
a.Largest Diamond: The 3,106 ct Cullinan diamond from South Africa in 1905 was cut and set in the British scepter b.Space Diamonds: Some meteorites contain hexagonal diamonds that are harder than those on Earth c.Cultured diamonds: HPHT (high temperature and pressure) and CVD (chemical vapor deposition) techniques can now produce 3 ct flawless diamonds


